Short Bowel Syndrome In Pediatrics
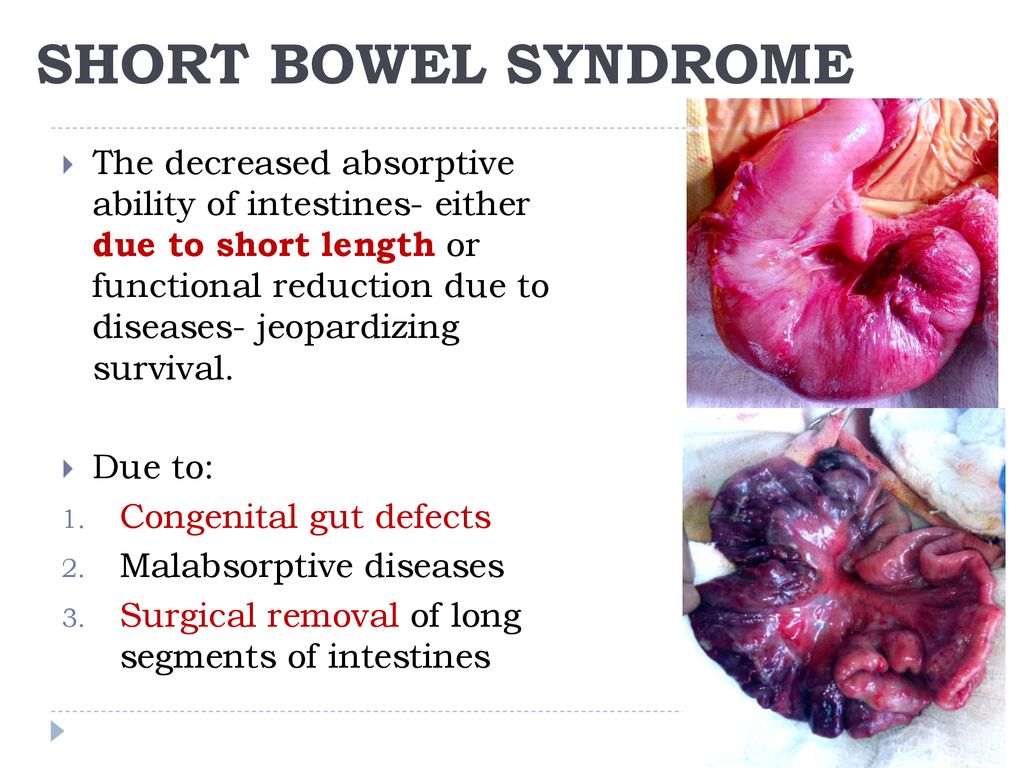
Short bowel syndrome in pediatrics. SBS is by far the most common cause of intestinal failure in infants and children. Short bowel syndrome is most commonly associated with the surgical removal resection of half or more of the small intestine. In order to achieve this intestinal adaptation must occur with resulting structural and functional changes.
How we care for short bowel syndrome. Symptoms of short bowel syndrome include. SBS can incur significant morbidity and mortality including intestinal failure cholestasis sepsis and death.
What is Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome Short Gut. Short bowel syndrome SBS is the most common cause of pediatric intestinal failure. What are the signs and symptoms of Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome Short Gut.
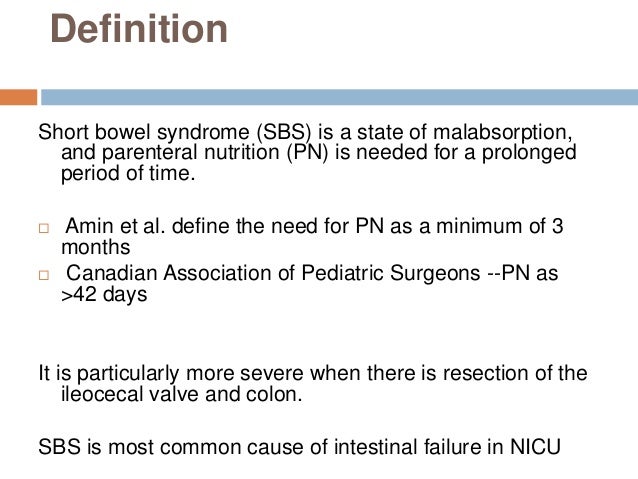
Short bowel syndrome SBS is a malabsorptive state that may occur either after surgical bowel resection or as the result of congenital bowel anomalies. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. Etiology and prognosis of pediatric short bowel syndrome.
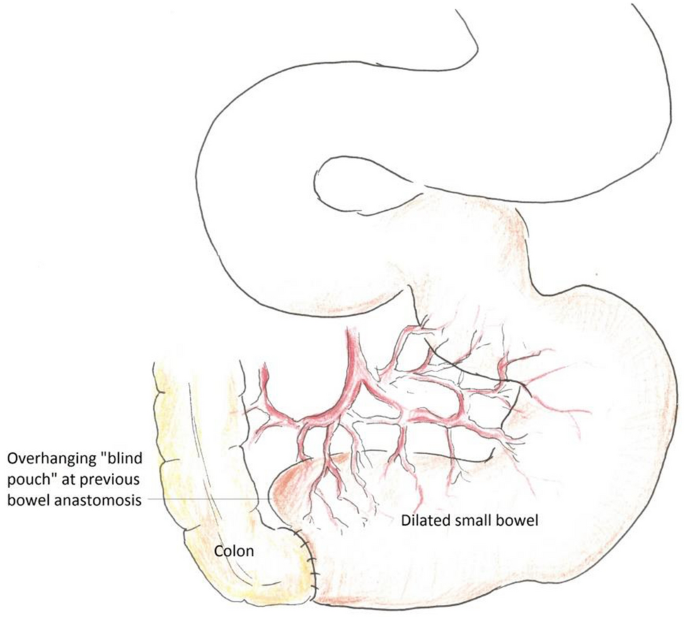
Pediatric short bowel syndrome SBS is a serious condition which occurs in children with congenital or acquired reduc tion in length of the small intestine. Select article Organization and outcomes of multidisciplinary intestinal failure teams. SBS results in excessive fluid loss.
The main symptoms of short bowel syndrome in children include diarrhea and failure to gain weight. Short bowel syndrome short gut is most often due to a birth defect or due to surgical removal of part of the bowel. Children with short bowel syndrome cannot get enough water vitamins and other nutrients from food to thrive.
Excessive gas andor foul-smelling stool. Intestinal rehabilitation programs in the management of pediatric intestinal failure and short bowel syndrome.
What is Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome Short Gut.
Pediatric short bowel syndrome SBS is a serious condition which occurs in children with congenital or acquired reduction in length of the small intestine. Excessive gas andor foul-smelling stool. Merritt RJ Cohran V Raphael BP et al. SBS results in excessive fluid loss. Resolution of parenteral nutrition-associated jaundice on changing from a soybean oil emulsion to a complex mixed-lipid emulsion. In order to achieve this intestinal adaptation must occur with resulting structural and functional changes. Children with short bowel syndrome cannot get enough water vitamins and other nutrients from food to thrive. The Fecal Microbiome in Pediatric Patients With Short Bowel Syndrome. 1Department of Pediatrics Baylor College of Medicine Houston Texas.
The treatment of infants and children with short bowel syndrome aims at restoring the intestinal continuity and at improving the physiological process of gut adaptation. The Fecal Microbiome in Pediatric Patients With Short Bowel Syndrome. Short bowel syndrome SBS is a malabsorptive state that may occur either after surgical bowel resection or as the result of congenital bowel anomalies. Etiology and prognosis of pediatric short bowel syndrome Pediatric intestinal failure is a complex and devastating condition defined as the inability of the intestine to absorb an adequate amount of fluid and nutrients to sustain life. SBS results in excessive fluid loss nutrient malabsorption electrolyte abnormalities increased susceptibility to infections parenteral nutrition associated complications and affects weight. Intestinal rehabilitation programs in the management of pediatric intestinal failure and short bowel syndrome. What is Pediatric Short Bowel Syndrome Short Gut.



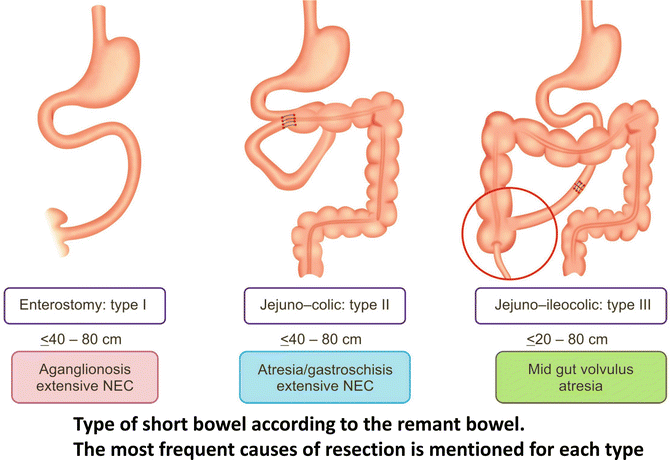


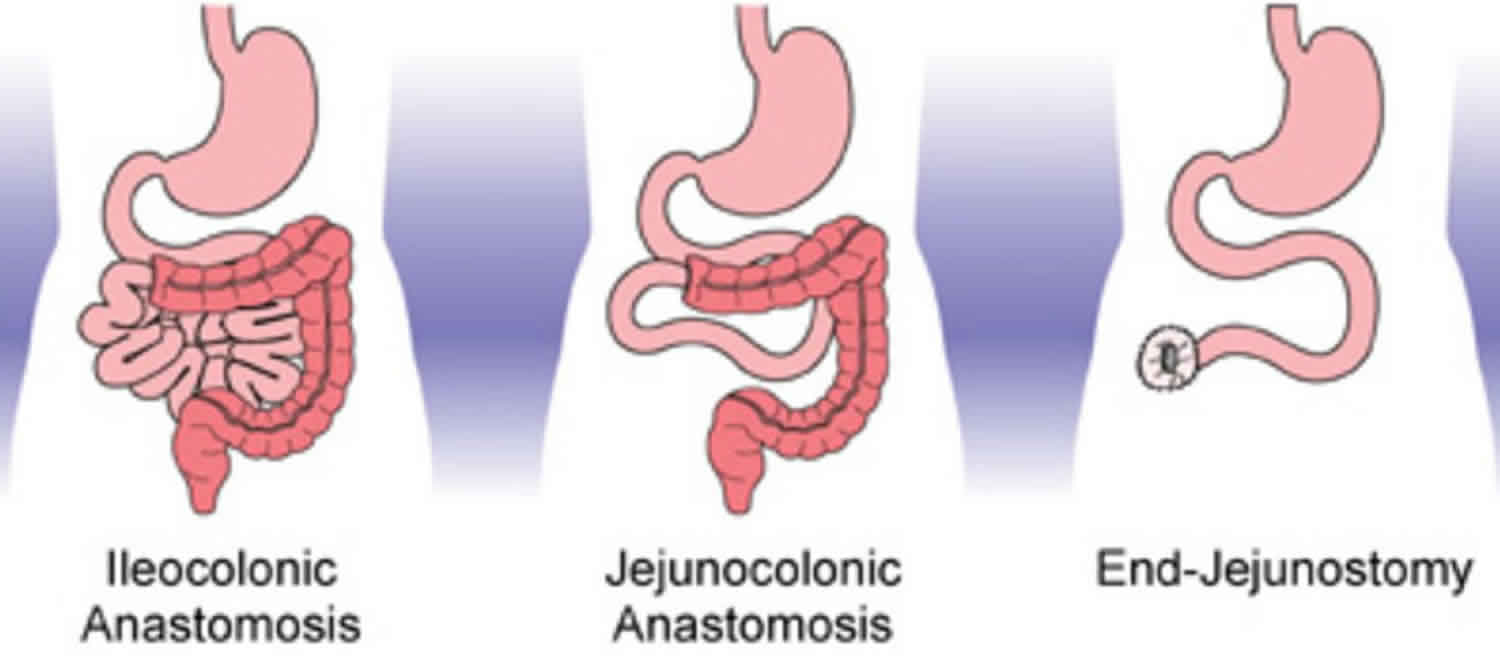










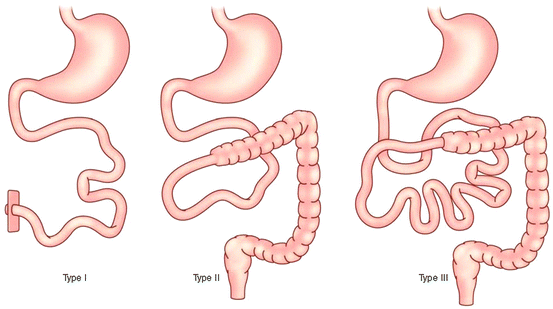






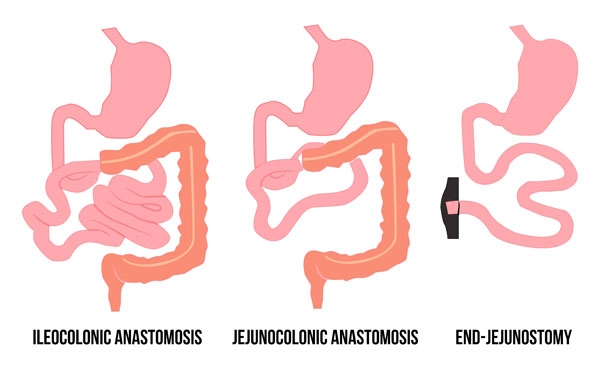












Post a Comment for "Short Bowel Syndrome In Pediatrics"